Perform Q-quantile normalization. More...
#include <yat/normalizer/qQuantileNormalizer.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| template<typename ForwardIterator > | |
| qQuantileNormalizer (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, unsigned int Q) | |
| Constructor. More... | |
| template<typename RandomAccessIterator1 , typename RandomAccessIterator2 > | |
| void | operator() (RandomAccessIterator1 first, RandomAccessIterator1 last, RandomAccessIterator2 result) const |
| Perform the Q-quantile normalization. More... | |
Detailed Description
Perform Q-quantile normalization.
Perform a Q-quantile normalization on a source range, after which it will approximately have the same distribution of data as the target range (the Q-quantiles are the same). The rank of an element in the source range is not changed.
The class works also with unweighed ranges, and there is no restriction that weighted source range requires weighted target range or vice versa.
Normalization goes like this:
- Data are not assumed to be sorted.
- Partition sorted target data in Q parts. Q must be 3 or larger because of requirements from the underlying cubic spline fit
- Calculate the arithmetic (weighted) mean for each part, the mean is assigned to the mid point of each part.
- Do the above for the data to be transformed (called source here).
- For each part, calculate the difference between the target and the source. Now we have Q differences
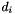 with associated rank (midpoint of each part).
with associated rank (midpoint of each part). - Create a cubic spline fit to this difference vector d. The resulting curve is used to recalculate all values in source.
- Use the cubic spline fit for values within the cubic spline fit range [midpoint 1st part, midpoint last part].
- For data outside the cubic spline fit use linear extrapolation, i.e., a constant shift.
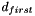 for points below fit range, and
for points below fit range, and 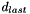 for points above fit range.
for points above fit range.
- Since
- New in yat 0.5
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
| theplu::yat::normalizer::qQuantileNormalizer::qQuantileNormalizer | ( | ForwardIterator | first, |
| ForwardIterator | last, | ||
| unsigned int | Q | ||
| ) |
Constructor.
Divides a sorted copy of range [first,last) into Q parts. Parts are divided such that the sum of weights is approximately the same in the different parts. If a relative weight, 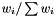 , is larger than 1/Q this might be difficult to achieve, in which case a an exception is thrown. In the unweighted case this implies that Q should be smaller (or equal) than number of elements in [first, last).
, is larger than 1/Q this might be difficult to achieve, in which case a an exception is thrown. In the unweighted case this implies that Q should be smaller (or equal) than number of elements in [first, last).
The range supplied to the constructor sets the target distribution.
As the source range is also divided into Q parts (when operator() is called), it is recommended to keep Q smaller (or equal) than the size of ranges that will be normalized.
Also, Q must not be smaller than 3 due to restrictions in the cubic spline fit utilized in the normalization.
Type Requirements:
ForwardIteratoris a model of Forward Traversal IteratorForwardIteratoris a Data Iterator
Member Function Documentation
| void theplu::yat::normalizer::qQuantileNormalizer::operator() | ( | RandomAccessIterator1 | first, |
| RandomAccessIterator1 | last, | ||
| RandomAccessIterator2 | result | ||
| ) | const |
Perform the Q-quantile normalization.
Elements in [first, last) are normalized as described above and the result is assigned to [result, result + last-first). Input range [first, last) is not modified. If ranges are weighted, the weights are copied from [first, last) to result range.
It is possible to normalize "in place"; it is permissible for first and result to be the same. However, as assignment occurs sequentially, the operation is undefined if result is the same as any in range [first, last).
Type Requirements:
RandomAccessIterator1is a Data IteratorRandomAccessIterator1is a Random Access Traversal IteratorRandomAccessIterator2is a Data IteratorRandomAccessIterator2is a Random Access Traversal IteratorRandomAccessIterator2is a Writable Iterator
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- yat/normalizer/qQuantileNormalizer.h
 1.8.5
1.8.5