Base class for interfacing GSL interpolation. More...
#include <yat/regression/GSLInterpolation.h>

Public Member Functions | |
| GSLInterpolation (const gsl_interp_type *, const utility::VectorBase &x, const utility::VectorBase &y) | |
| The default constructor. More... | |
| virtual | ~GSLInterpolation (void)=0 |
| The destructor. | |
| double | evaluate (double x) |
| Calculate the interpolated value for x. More... | |
| double | evaluate_derivative (double x) |
| Calculate the derivative of the interpolated function at x. More... | |
| double | evaluate_derivative2 (double x) |
| Calculate the 2nd derivative of the interpolated function at x. More... | |
| double | evaluate_integral (double a, double b) |
Calculate the numerical integral of the interpolated function over the range ![$ [a,b] $](form_169.png) . More... . More... | |
| double | evaluation (void) const |
| The result of the latest evaluaion function call is stored and can be retrieved with this function. More... | |
| unsigned int | min_size (void) const |
| This function returns the minimum number of points required by the interpolation type. More... | |
Detailed Description
Base class for interfacing GSL interpolation.
The GSL interpolation is described in the GSL Manual. The GSL library provides a variety of interpolation methods, including Cubic splines and Akima splines. Interpolations can be defined for both normal and periodic boundary conditions. Additional functions are available for computing derivatives and integrals of interpolating functions.
Given a set of data points  the sub classes compute a continuous interpolating function
the sub classes compute a continuous interpolating function 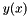 such that
such that 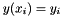 . The interpolation is piecewise smooth, and its behavior at the end-points is determined by the type of interpolation used.
. The interpolation is piecewise smooth, and its behavior at the end-points is determined by the type of interpolation used.
When underlying GSL functions return GSL error an GSL_error is thrown. Refer to the gsl_errno.h for the error code listing.
- Since
- New in yat 0.5
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
| theplu::yat::regression::GSLInterpolation::GSLInterpolation | ( | const gsl_interp_type * | , |
| const utility::VectorBase & | x, | ||
| const utility::VectorBase & | y | ||
| ) |
The default constructor.
Initialization of the interpolation object for the data 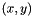 where x and y are vector like objects of the same size. The content of x and y are copied for internal storage. x is always assumed to be strictly ordered, with increasing x values; the behavior for other arrangements is not defined.
where x and y are vector like objects of the same size. The content of x and y are copied for internal storage. x is always assumed to be strictly ordered, with increasing x values; the behavior for other arrangements is not defined.
- Exceptions
-
GSL_error if some underlying GSL functions return GSL error. Refer to gsl_errno.h for the error code listing.
Member Function Documentation
| double theplu::yat::regression::GSLInterpolation::evaluate | ( | double | x | ) |
Calculate the interpolated value for x.
- Returns
- The interpolated value of
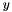 for a given point x.
for a given point x.
- Exceptions
-
GSL_error if evaluation is requested outside the range defined by the interpolation algorithm.
| double theplu::yat::regression::GSLInterpolation::evaluate_derivative | ( | double | x | ) |
Calculate the derivative of the interpolated function at x.
- Returns
- The derivative.
- Exceptions
-
GSL_error if evaluation is requested outside the range defined by the interpolation algorithm.
| double theplu::yat::regression::GSLInterpolation::evaluate_derivative2 | ( | double | x | ) |
Calculate the 2nd derivative of the interpolated function at x.
- Returns
- The 2nd derivative.
- Exceptions
-
GSL_error if evaluation is requested outside the range defined by the interpolation algorithm.
| double theplu::yat::regression::GSLInterpolation::evaluate_integral | ( | double | a, |
| double | b | ||
| ) |
Calculate the numerical integral of the interpolated function over the range ![$ [a,b] $](form_169.png) .
.
- Returns
- The integral.
- Exceptions
-
GSL_error if evaluation is requested outside the range defined by the interpolation algorithm.
| double theplu::yat::regression::GSLInterpolation::evaluation | ( | void | ) | const |
The result of the latest evaluaion function call is stored and can be retrieved with this function.
- Returns
- The latest evaluated value.
| unsigned int theplu::yat::regression::GSLInterpolation::min_size | ( | void | ) | const |
This function returns the minimum number of points required by the interpolation type.
For example, Akima spline interpolation requires a minimum of 5 points.
- Returns
- The minimum number of points required.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- yat/regression/GSLInterpolation.h
 1.8.5
1.8.5