Kolmogorov Smirnov Test for one class. More...
#include <yat/statistics/KolmogorovSmirnovOneSample.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| KolmogorovSmirnovOneSample (void) | |
| Constructor. | |
| void | add (double value, double weight=1.0) |
| add a value More... | |
| double | p_value (void) const |
| Large-Sample Approximation. More... | |
| void | remove (double value, double weight=1.0) |
| Remove a data point. More... | |
| void | reset (void) |
| resets everything to zero | |
| double | score (void) const |
| Kolmogorov Smirnov statistic. More... | |
| double | signed_score (void) const |
Friends | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &, const KolmogorovSmirnovOneSample &) |
Detailed Description
Kolmogorov Smirnov Test for one class.
Class can be used to test if data follows standard uniform distribution. Other distributions are not supported directly, but it is possible to check against other distribution by tranforming the data. If, for example, X is standard exponentially distributed log(X) is standard uniform. Therefore, rather than testing if X is exponential it is equivalent to test if log(X) is standard uniform.
- Since
- New in yat 0.11
Member Function Documentation
| void theplu::yat::statistics::KolmogorovSmirnovOneSample::add | ( | double | value, |
| double | weight = 1.0 |
||
| ) |
add a value
value should be a value in range [0, 1].
| double theplu::yat::statistics::KolmogorovSmirnovOneSample::p_value | ( | void | ) | const |
Large-Sample Approximation.
This analytical approximation of p-value can be used when all weight equal unity and sample size n is large. The p-value is calcuated as 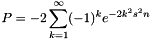 , where s is the score and n is the sum of weights.
, where s is the score and n is the sum of weights.
| void theplu::yat::statistics::KolmogorovSmirnovOneSample::remove | ( | double | value, |
| double | weight = 1.0 |
||
| ) |
Remove a data point.
- Exceptions
-
utility::runtime_error if no data point exist with value and weight.
| double theplu::yat::statistics::KolmogorovSmirnovOneSample::score | ( | void | ) | const |
Kolmogorov Smirnov statistic.
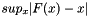 where is the empirical cumulative distribution
where is the empirical cumulative distribution 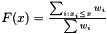
| double theplu::yat::statistics::KolmogorovSmirnovOneSample::signed_score | ( | void | ) | const |
Same as score() but keeping the sign, in other words, abs(signed_score())==score()
A positive score implies that values on average are smaller 0.5.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- yat/statistics/KolmogorovSmirnovOneSample.h
 1.8.5
1.8.5