ThePEG::Amplitude Class Reference
The Amplitude class is the abstract base class for all the classes representing complex amplitudes associated with either a hard 2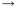 N subprocess or a decay 1
N subprocess or a decay 1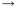 N process.
More...
N process.
More...
#include <Amplitude.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| Amplitude & | operator= (const Amplitude &) |
| Private and non-existent assignment operator. | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static void | Init () |
| Standard Init function used to initialize the interfaces. | |
Static Public Attributes | |
|
static AbstractNoPIOClassDescription < Amplitude > | initAmplitude |
| Describe an abstract base class with persistent data. | |
Private Member Functions | |
Main virtual functions to be overridden by sub-classes. | |
| virtual Complex | value (const tcPDVector &particles, const vector< Lorentz5Momentum > &momenta, const vector< int > &helicities)=0 |
| Return the amplitude. | |
| virtual Complex | overestimateValue (const tcPDVector &particles, const vector< Lorentz5Momentum > &momenta, const vector< int > &helicities) |
| Return an overestimated amplitude. | |
Alternative interface to main virtual functions. | |
| Complex | value (const PVector &particles, const vector< int > &helicities) |
| Return the amplitude. | |
| Complex | overestimateValue (const PVector &particles, const vector< int > &helicities) |
| Return an overestimated amplitude. | |
Detailed Description
The Amplitude class is the abstract base class for all the classes representing complex amplitudes associated with either a hard 2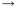 N subprocess or a decay 1
N subprocess or a decay 1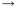 N process.
N process.
The returned value should be dimensionless suitable scaled by the total invariant mass squared (shat), which is always computable from the specified momenta of the particles in the vertex. Notice that the amplitude for splitting 1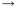 N processes is instead represented in other classes (derived from the SplitFun class).
N processes is instead represented in other classes (derived from the SplitFun class).
- See also:
- The interfaces defined for Amplitude.
Definition at line 34 of file Amplitude.h.
Member Function Documentation
| virtual Complex ThePEG::Amplitude::value | ( | const tcPDVector & | particles, | |
| const vector< Lorentz5Momentum > & | momenta, | |||
| const vector< int > & | helicities | |||
| ) | [private, pure virtual] |
Return the amplitude.
Given the ParticleData objects in particles, their momenta and helicities of all the particles in the vertex, return the complex amplitude. The convention is the order of the vectors is that first there is the incoming particle(s) and then the outgoing ones. For the helicities, the convention is to number them starting from 0 (no negative values, because they are used as vector indeces), for example, for a massive particle of spin S, 0 <= helicity <= 2*S. The returned value should be dimensionless suitable scaled by the total invariant mass squared (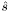 ), which is always computable from the specified momenta of the particles in the vertex.
), which is always computable from the specified momenta of the particles in the vertex.
| virtual Complex ThePEG::Amplitude::overestimateValue | ( | const tcPDVector & | particles, | |
| const vector< Lorentz5Momentum > & | momenta, | |||
| const vector< int > & | helicities | |||
| ) | [private, virtual] |
Return an overestimated amplitude.
Same as value(const tcPDVector &, const vector<Lorentz5Momentum> &, const vector<int> &), but it provides an overestimate of the complex amplitude, that is: abs( overestimaValue() ) >= abs(value()) The default definition just returns value(), but it can be overriden by derived classes.
| Complex ThePEG::Amplitude::value | ( | const PVector & | particles, | |
| const vector< int > & | helicities | |||
| ) | [private] |
Return the amplitude.
Calls value(const tcPDVector &, const vector<Lorentz5Momentum> &, const vector<int> &) and should not be overridden.
| Complex ThePEG::Amplitude::overestimateValue | ( | const PVector & | particles, | |
| const vector< int > & | helicities | |||
| ) | [private] |
Return an overestimated amplitude.
Calls overestimateValue(const tcPDVector &, const vector<Lorentz5Momentum> &, const vector<int> &)
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
 1.5.5
1.5.5